Motor rotor dynamic balance process control points
Published:
2019-07-03 11:38
Unbalanced rotor is one of the main causes of excessive rotor vibration and noise, which directly affects the performance and service life of the engine. Due to defects in the electrical design of the motor, noise and vibration are exceeded, and the mechanical imbalance is intertwined, resulting in extremely complicated motor noise and vibration problems. Today, Xiaobian discusses with you the imbalance of the motor rotor itself, that is, the electromagnetic factors are opened, and the mechanical sources of noise and vibration problems are specifically explored.
The rotor of the motor itself is a typical rotor. Uncertainty in processing or manufacturing, such as processing deviations or manual operations, results in uneven mass distribution (ie, eccentricity), resulting in an imbalance. If the force generated by the imbalance is not corrected, not only will the support bearing be damaged, the motor be damaged, but also the machine base will be cracked and the structural part weld will be cracked.

By increasing or de-emphasizing, reducing or even eliminating this imbalance is called rotor balance. When the unbalanced mass moment exists on the radial plane where the centroid is located, and there is no force moment present, the radial plane directly increases or decreases the weight through the centroid, which is called static balance correction; if the centroid of the rotor is just on the axis The center of gravity of the rotor on both sides of the axis of the centroid is not on the axis. When rotating, the two centrifugal forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, forming a pair of couples. This moment causes the cyclical change of the two-end bearing, so it must be at the center of mass. The weighting or weight reduction on the two planes at both ends is called dynamic and static balance correction. Normally, the centrifugal force is a resultant force and a force couple when the rotor of the motor rotates. Therefore, the rotor dynamic balance is often said to be a corrective operation of dynamic and static mixing imbalance.

Rotor calibration balance method
The centrifugal force generated by the imbalance depends on the speed and weight of the rotor. In order to obtain the correspondence between the unbalanced mass and the amplitude, the test weight can be used to change the vibration amplitude, and it is known how much amplitude change is caused by the unit unbalanced weight.
Assuming that A is the original amplitude (μm), G is the rotor weight (kg), R is the equilibrium radius (mm), and the rotational speed is n (r/min), then the test weight is estimated by the following formula:
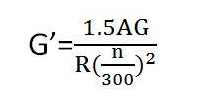
The weighting position mainly relies on the experience accumulation to determine the weighting direction of the test, and the general unbalanced weight advances the vibration point by 15-45°.
Balance accuracy and its calculation
Balance accuracy, also called balance quality, is an indicator of the strength of the rotor balance, in mm/s. If the unbalance ratio (unit g.mm/kg) or the rotor eccentricity (unit μm) after the rotor balance is e, the balance accuracy G (unit: mm/s) is:
G = ωe/1000
Where ω is the rotor angular velocity (rad/s) and the relationship with the rotational speed n is ω=2πn/60
If the equilibrium radius is R (in mm), the formula for allowing the residual unbalance mass m (unit g) is derived as follows:
2mω2R=Wω2e
m=We/2R
Where W is the total mass of the rotor (in kg)
If there is a motor rotor, the balance accuracy is G6.3, the rotor speed is n=800r/min, the rotor mass is 0.142kg, and the rotor diameter is 17mm.
R=17/2=8.5(mm)
e=1000G/ω=30000G/πn=75.2(μm)
Allowable unbalance amount m=We/2R=0.63(g)
At present, Guangzhou Zhuo Xuan Jin dynamic balancing machine is a high efficiency balancing machine designed and developed by various motor manufacturers. There are automatic balancing machine and automatic positioning dynamic balancing machine; according to the measurement principle, there are hard support dynamic balancing machine and soft support dynamic balancing machine; according to the application, there are general and special dynamic balancing machines.
In the actual balance process, we can find that some rotors have no problems during the dynamic balance process, or the rotor has been determined by dynamic balance. In actual operation, vibration or noise due to the rotor itself may occur. It is more serious for the problem of the flexible rotor; in addition, the difference between the motor speed and the balance speed of the balancing device will also cause the balance effect to be inconsistent with the actual running effect. Based on the analysis and solution of many similar problems in the past, based on continuous experience accumulation and theoretical innovation, the fully automatic balancing machine, automatic positioning and balancing machine, circle-driven dynamic balancing machine, universal joint dynamic balancing machine, single and double-sided design Vertical dynamic balancing machine, self-driven complete motorized balancing machine, user's original dynamic balancing machine technology improvement and transformation, dynamic balance wearing parts, and special dynamic balancing machine tailored according to user's special workpiece requirements.
Related news
2018-12-03
In addition, if you need to buy a balance test machine, please contact us directly.
2018-12-03
Safety operation of the rotor of the motor to be balanced
电机转子装配工的一般操作规程如下: 1、工作前,整理场地,放稳各零、部件,并检查装配使用工具和工作环境是否安全良好。 2、吊放电机机座、底板、定子、转子、轴承等大型部件时必须放好方箱或垫木...
2018-12-03
Rubber roller dynamic balancing machine customer site
Mainly used in the balance correction of high-speed rotating workpieces in various household appliances
2018-12-03
Mainly used in micro-motor rotors, such as automotive motors, household electrical appliances, micro-motors
2018-12-03
[Guangzhou Zhuo Xuanjin] balance machine application range
Dynamic balancing machines are widely used and can be divided into ten categories
2018-12-03
Guangzhou Zhuo Xuanjin various balance machines and their application range
Mainly used in the balance correction of high-speed rotating workpieces in various household appliances, cooling fans, motors, generators, pumps, automobiles, printing, rollers and other industries.

