The rotor allows the assignment of correction surfaces for residual imbalance
Published:
2019-06-10 16:57
When the motor rotor has only one correction surface, the allowable residual imbalance value of this motor rotor is the allowable residual imbalance value of this correction surface.
For the motor rotor with two correction surfaces I, II, the permissible residual unbalance values UperI and UperII are allowed to assign the residual unbalance value Uper to the I, I correction planes, because the motor rotor correction surface and the bearing arrangement Different spacing can be divided into four different conditions. The vertical machining center spindle assembly is usually in the following conditions (see Figure 1).
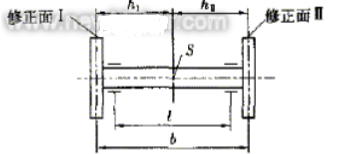
figure 1
S-- motor rotor quality center;
L-- spacing between bearings;
hI-- the distance between the calibration surface I and the center of the rotor mass;
hII-- the distance between the calibration surface II and the center of the rotor mass;
b=hI+hII-- The distance from the calibration plane I to the correction plane II.
When the motor rotor meets the following conditions:
The rotor mass of the motor is in the central part of the three-part distance between the bearings. When the two correction faces I, II clamp the two bearings on the outside of the two bearings:
Related news
2018-12-03
In addition, if you need to buy a balance test machine, please contact us directly.
2018-12-03
Safety operation of the rotor of the motor to be balanced
电机转子装配工的一般操作规程如下: 1、工作前,整理场地,放稳各零、部件,并检查装配使用工具和工作环境是否安全良好。 2、吊放电机机座、底板、定子、转子、轴承等大型部件时必须放好方箱或垫木...
2018-12-03
Rubber roller dynamic balancing machine customer site
Mainly used in the balance correction of high-speed rotating workpieces in various household appliances
2018-12-03
Mainly used in micro-motor rotors, such as automotive motors, household electrical appliances, micro-motors
2018-12-03
[Guangzhou Zhuo Xuanjin] balance machine application range
Dynamic balancing machines are widely used and can be divided into ten categories
2018-12-03
Guangzhou Zhuo Xuanjin various balance machines and their application range
Mainly used in the balance correction of high-speed rotating workpieces in various household appliances, cooling fans, motors, generators, pumps, automobiles, printing, rollers and other industries.

